Table of Contents
Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a revolutionary force permeating every aspect of our daily lives. From medical applications to industry, from finance to creativity, AI has demonstrated its transformative potential.
Enjoy:
- Over 60 AI tools to create quality content
- More time for creativity, stress-free
- Impactful content that attracts readers and visitors
All with just one click.
But as we explore how to harness artificial intelligence, we cannot ignore the challenges and ethical considerations that arise alongside this technological acceleration. In a world where AI is increasingly ubiquitous, we will explore how we can embrace this technology responsibly, seeking to define a path that leads to innovative and sustainable outcomes.
Fundamentals of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a technology that enables machines to mimic human cognitive abilities such as reasoning, learning, and planning through the use of algorithms. This technology is used to perform a wide range of tasks, including collecting and analyzing large amounts of data, as well as simulating human learning and intelligence processes.
There are different types of artificial intelligence, each with different characteristics. Among the main types of artificial intelligence are:
- Limited Artificial Intelligence (ANI), capable of performing specific tasks,
- General Artificial Intelligence (AGI), capable of performing a wide range of tasks similarly to humans,
- Superintelligent Artificial Intelligence (ASI), surpasses human intelligence in every field.
Strong and Weak Artificial Intelligence: Differences
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a complex field that presents two different perspectives: strong AI and weak AI. Weak AI focuses on mimicking how a human reasons in specific contexts, making decisions based on logical reasoning. This approach aims to emulate human thinking without trying to fully replicate human intelligence. It focuses on specific tasks and does not seek to develop autonomous consciousness.
Strong AI is extremely similar to human intelligence, as it aspires to emulate human thinking in a more abstract and autonomous way, acting and thinking effectively like a human in a wide range of contexts. This perspective aims to develop autonomous consciousness inspired by the functioning of the human brain, capable of dealing with any type of situation.
The applications of weak AI make humans perceive that machines act intelligently in limited contexts, providing effective solutions for specific tasks. On the contrary, strong AI aims to achieve a level of autonomy and complexity to think and act like a human in a broader sense, paving the way for new horizons in terms of artificial intelligence.
The key difference between the two approaches is not only their reasoning ability but also the level of consciousness and autonomy they seek to achieve. While weak AI is like a fine piece of engineering, strong AI is more akin to a form of artificial life. Both fields are extremely interesting and promising, bringing significant benefits in various sectors such as medicine, industrial automation, cybersecurity, and many others. However, it is crucial to understand the differences between the two perspectives to fully harness the potential of artificial intelligence and ensure its safe and ethical development.
Understanding the differences between these two approaches is important to grasp how to leverage artificial intelligence in our favor and in various contexts.
Machine Learning and Neural Networks
Machine learning, also known as deep learning, is a branch of artificial intelligence that focuses on developing algorithms that allow computers to learn and improve from experiences without being explicitly programmed. In other words, it is about teaching computers to make decisions based on data without being specifically programmed for each situation.
Neural networks are a specific type of machine learning method based on artificial structures inspired by the functioning of the human brain. This allows computers to learn from examples, both in supervised and unsupervised ways, and improve their performance over time.
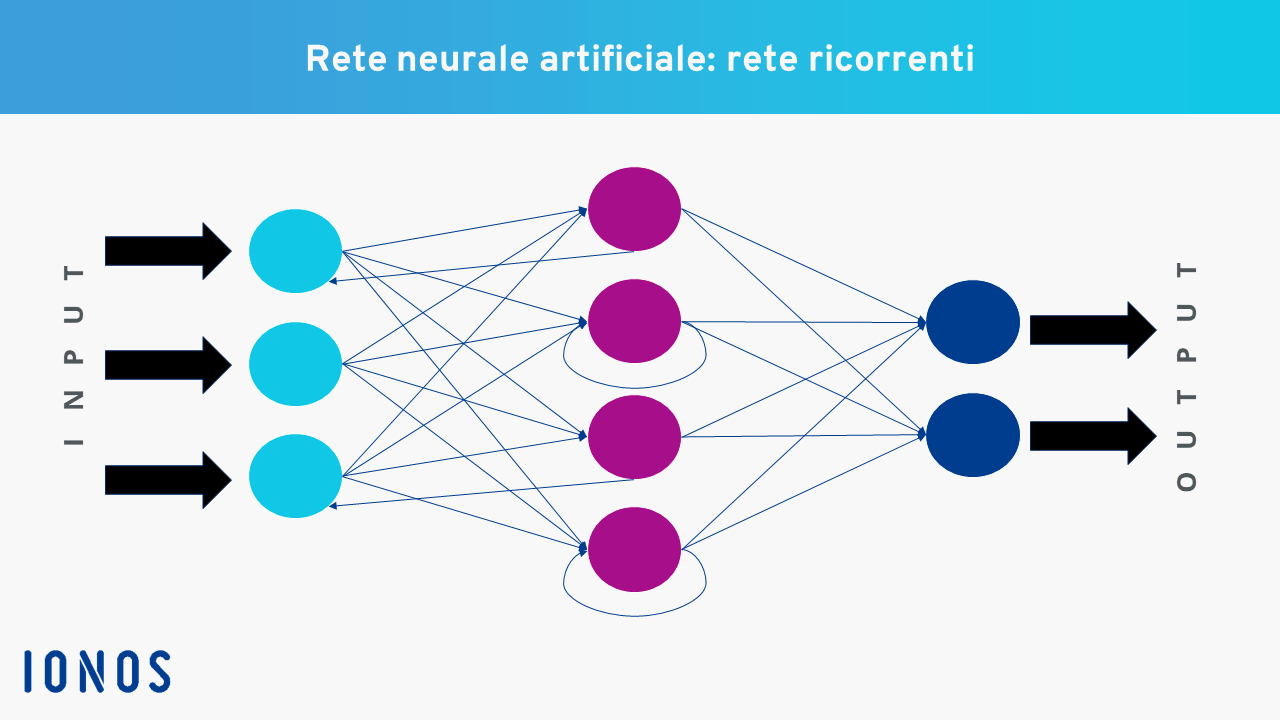
Artificial neural networks, which are fundamental in machine learning, can be classified into different types, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN). Convolutional Neural Networks are particularly effective in processing three-dimensional data, mainly used for image classification and object recognition.
Deep learning is a subcategory of machine learning that relies on models of deeper and more complex neural networks. This approach allows computers to learn from large amounts of data more efficiently and achieve more accurate results in tasks such as image recognition, automatic translation, and much more. Deep learning, being based on deeper and more complex neural networks, has revolutionized the approach to machine learning, enabling computers to analyze and process vast amounts of data with unprecedented precision and efficiency.
Thanks to this, artificial intelligence can perform increasingly complex tasks and provide innovative solutions in sectors such as medicine, industrial automation, financial market analysis, and many others. The evolution of deep learning continues to be a stimulating and constantly developing field, with great potential to radically transform our society.
Convolutional Neural Networks: What Are They?
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), also known as ConvNets, are a type of artificial neural network architecture specialized in processing three-dimensional data, mainly used for image classification and object recognition. Convolutional Neural Networks are particularly effective in processing three-dimensional data, mainly used for image classification and object recognition.
- “Structure of Convolutional Neural Networks: CNNs are mainly composed of three types of layers:
- Convolutional layer: This is the heart of CNN, where convolution takes place. A filter (or kernel) moves through the image, applying convolution operations and producing feature maps. This layer is essential for recognizing basic features such as edges and colors.
- Pooling layer: This layer reduces the dimensionality of the input by decreasing the number of parameters. The two main pooling techniques are maximum and average pooling, helping maintain salient features while reducing complexity.
- Fully Connected (FC) layer: This layer performs classification based on the functions extracted from the previous layers. Each node in this layer is directly connected to a node in the previous layer.
- Functioning of CNN:
- Convolution: Uses a filter to perform convolution on the input image, producing feature maps.
- ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit): After each convolution, a ReLU function is applied to introduce non-linearity.
- Pooling: Reduces the input’s dimensionality, retaining the most relevant features.
- Hierarchical structure: The combination of convolutional and pooling layers creates a hierarchical structure, progressively identifying more complex features.
- Applications of CNNs: Convolutional Neural Networks form the basis for image recognition and computer vision. They find applications in various areas, including marketing (facial recognition on social media), healthcare (radiological diagnosis), retail (visual search), the automotive sector (autonomous driving technologies), and many others.
Practical Applications of AI: How to Harness Artificial Intelligence in Different Sectors

When considering how to leverage artificial intelligence, it’s essential to remember that today, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in various sectors is leading to an unprecedented transformation, changing the way businesses operate and generating new forms of innovation. This phenomenon is bringing about a revolution in terms of business models, marketing strategies, production processes, and customer interaction.
In fact, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has found applications in various fields, including medicine, automotive, the financial sector, and manufacturing. In medicine, AI is used to assist doctors in diagnosis, through algorithms that analyze medical data to detect diseases more quickly and accurately. This improves the accuracy of diagnoses and reduces waiting times for patients.
In the automotive industry, AI is used for autonomous driving systems that interpret and respond to environmental stimuli. This helps redefine the concept of mobility, introducing new possibilities for transportation and road safety.
In the financial sector, AI is employed to analyze markets and provide more accurate forecasts, supporting investment decisions. This can help market operators make more informed decisions and better manage financial risk.
In manufacturing, AI is used for predictive maintenance, optimizing interventions and reducing machine downtime, improving overall operational efficiency.
Even in the education sector, AI is opening up new possibilities, such as adapting learning paths based on students’ needs.
In the marketing field, AI is used to analyze consumer data and create personalized marketing strategies.
These examples represent only a small part of the potential of AI in radically transforming our interaction with the world. AI has the potential to bring significant changes in various areas, improving processes and introducing new modes of interaction and processing.
Regardless of the sector it fits into, discovering how to leverage artificial intelligence is generating great curiosity, and the impact of these new strategies is having a significant effect, allowing for improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and user experience. However, it is important to also consider the ethical and social implications of these innovations, ensuring that AI is used responsibly and in line with human values.
Business Transformation and Innovation Drive:
The adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) in businesses is a revolutionary change in business processes, not just a simple technological adaptation. The ability of AI to analyze large amounts of data in real-time allows companies to manage their resources more informedly and targeted. This leads to an increase in operational efficiency, as repetitive tasks can be entrusted to intelligent systems, and human resources can be freed up for more creative and strategic activities.
At the same time, AI acts as a catalyst for innovation. Thanks to machine learning, businesses can anticipate market trends, adapt quickly to consumer needs, and develop cutting-edge products and services. In this way, AI becomes the driving force behind new business models, pushing companies beyond traditional limits.
In this dynamic context, understanding how to leverage artificial intelligence is equivalent to realizing that AI is not just a technological tool; it is the beating heart of a business transformation that redefines how we operate, innovate, and grow. The increasingly widespread adoption of AI opens the doors to a future where synergistic collaboration between artificial intelligence and human ingenuity becomes the key to success.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Understanding how to leverage artificial intelligence is a complex and challenging task that requires significant attention to both technology and its ethical implications. In this process, it is crucial to carefully consider issues related to privacy and data security. The collection, processing, and use of data are central to the implementation of AI, and therefore, it is important to ensure the protection of personal and sensitive information.
To address this challenge, it is necessary to adopt responsible and transparent approaches in data management. This involves creating clear protocols and policies to ensure that data is used ethically and lawfully. Furthermore, it is crucial to consider the social implications of AI and work towards solutions that respect human rights and dignity.
In addition to ethical and legal issues, understanding how to leverage artificial intelligence and implementing it also requires a broad consideration of practical and technological implications. Data security and protection against cybercrime are essential to ensure that AI is used safely and effectively. Moreover, data quality and transparency in the learning algorithm are crucial to ensuring accurate and reliable results.
In summary, the implementation of AI goes beyond simply adopting advanced technologies; it is, in fact, a complex process that requires thoughtful reflection on ethical, legal, practical, and technological aspects. Addressing these challenges responsibly and conscientiously is essential to ensure that AI is used safely, fairly, and ethically.
It is important to emphasize that AI is continuously evolving, and its deployment raises not only ethical questions but also concerns about potential societal and employment consequences. While it can lead to an improvement in living conditions and economic performance, it could also result in the replacement of certain professional roles and the acceleration of social inequalities.
The ethical aspect of artificial intelligence is of fundamental importance, as this technology influences various aspects of our society. A relevant issue is the lack of transparency in algorithms.
It is necessary to promote transparency and accountability in the use of artificial intelligence, ensuring that the decisions made are understandable and based on ethical principles.
You can delve into the topic in our article where we discussed ethics and artificial intelligence.
Maximizing AI Benefits: Practical Tips for Businesses and Professionals
Understanding how to leverage artificial intelligence is as crucial as having a clear understanding of specific needs when implementing Artificial Intelligence (AI) within a company or professional practice. This means identifying areas where AI could bring added value, such as optimizing business processes, personalizing offered services, or conducting predictive analyses.
Customizing services might involve using AI to tailor products or services based on the specific needs of each customer. While predictive analysis could enable predicting future trends or customer behaviors, providing valuable insights for business decisions.
Understanding specific needs also involves considering available resources and the skills required to successfully implement AI within the company or professional practice. Once specific needs are clearly understood, it will be possible to develop an AI implementation strategy aimed at effectively meeting those needs.
Training and Awareness: It is important to adequately train staff to understand and fully harness the potential of artificial intelligence. This can be beneficial for the organization as it helps ensure a more effective adoption of the technology. Furthermore, it enables professionals to collaborate synergistically with AI to achieve the best possible results.
Staff training on AI may include learning new technical skills related to data management and analysis, as well as understanding AI models and their practical applications.
Human-Machine Collaboration: Artificial intelligence is a technology that simulates human intelligence through software and algorithms. It can be used to automate tasks that involve repetitiveness and data analysis. This means people can be freed from tedious tasks and focus on activities that require creativity and strategy. This can lead to increased productivity and efficiency in the workplace.
People must be able to understand how AI works, how to use it effectively, and how to interpret the results obtained. Furthermore, it is also important to ensure that AI is used responsibly and ethically to avoid potential negative consequences
Integration with Other Technologies: This combination can lead to more overall benefits and the creation of advanced, interconnected solutions This means that using AI alongside IoT and blockchain can result in more effective and cutting-edge systems.
Integrating AI with IoT could, for example, allow the creation of devices that can learn from collected data and adapt in real-time to the situations they are placed in. Moreover, AI could be used to analyze and interpret data from IoT devices more efficiently, providing more accurate and useful results.
The combination of AI and blockchain could lead to more secure and transparent solutions, allowing verification and traceability of information in innovative ways. For instance, AI could be used to identify and prevent fraud or unauthorized access within blockchain-based systems.
Cost-Benefit Assessment: Before implementing any project, it is fundamental to conduct a thorough cost-benefit assessment. This means it is important to understand clearly how much investment will be required and what the expected returns will be. This will allow for strategic and informed planning, avoiding surprises or mistakes in project implementation.
The cost-benefit assessment is useful not only to understand the financial details of project implementation but also to identify potential risks and opportunities. This way, a more comprehensive and realistic view of the project’s impact on the organization and the surrounding environment can be obtained.
Conclusions
We have seen that artificial intelligence emerges as a driving force capable of profoundly revolutionizing our society and business dynamics. Through the exploration of its applications in various sectors, AI integrates into medicine, industry, finance, and many other fields, bringing significant innovations with it.
However, this path towards widespread adoption of AI is not without challenges, and it is imperative to address these challenges with an ethical perspective, ensuring that AI contributes to social progress without compromising fundamental values.
AI is not just a technology but a strategic partner in shaping the future. With responsible management, it will not completely replace human work but rather collaborate with it to create added value in industries and businesses.
